EPOS | VC – Volcanic Ash Modelling
The Volcanology (VC) test case, has been developed in order to extend the use of the DARE platform to the EPOS volcanology community.
The scientific purpose of the test case is to analyse ash dispersal after volcanic eruptions including distributions of deposit thickness, ground load and airborne mass. A fast and reliable simulation of these volcanic parameters and their mapping onto the affected area is an important procedure in volcanic hazard modelling. The DARE platform, together with its user friendly and platform independent execution, can support domain specialists in achieving these tasks, demonstrating its utility also in the framework of the volcanic hazard and risk assessment.
Figure 5 shows the detailed steps of the VC workflow and how they are implemented and executed in the DARE platform:
- Users set the eruption parameters (volcanic source, area, time) in the file Input.json and upload this file in the DARE shared file system.
- Based on information in 1., the users prepare the required regional meteorological data for the selected eruption time, as well as the local digital elevation model (DEM) where ETOPO1 is currently supported. The meteorological data are freely available by downloading them from NOAA or ECMWF/ERA5 in daily or monthly means. This step is implemented as a dispel4py workflow and executed in the platform via a corresponding API call.
- Using the inputs in 1. and 2., the simulations to obtain ash dispersal distributions are run with the code FALL3DPy, a python port of the original Fortran code FALL3D by [Folch et al. 2009]. In DARE the dockerized version of FALL3DPy is used and the specific steps to run a simulation are described by a CWL workflow launched via an appropriate API call.
- In the post-processing step the content of NetCDF files together with the user input is used to generate visualisations of the individual ash distributions. This step is implemented as a dispel4py workflow and executed in the platform via a corresponding API call.
- Output products are stored with their metadata and provenance.
Metadata and provenance are captured and stored for all the workflows through dispel4py and CWL, and they are fully customisable and explorable through the Provenance Viewer Portal.
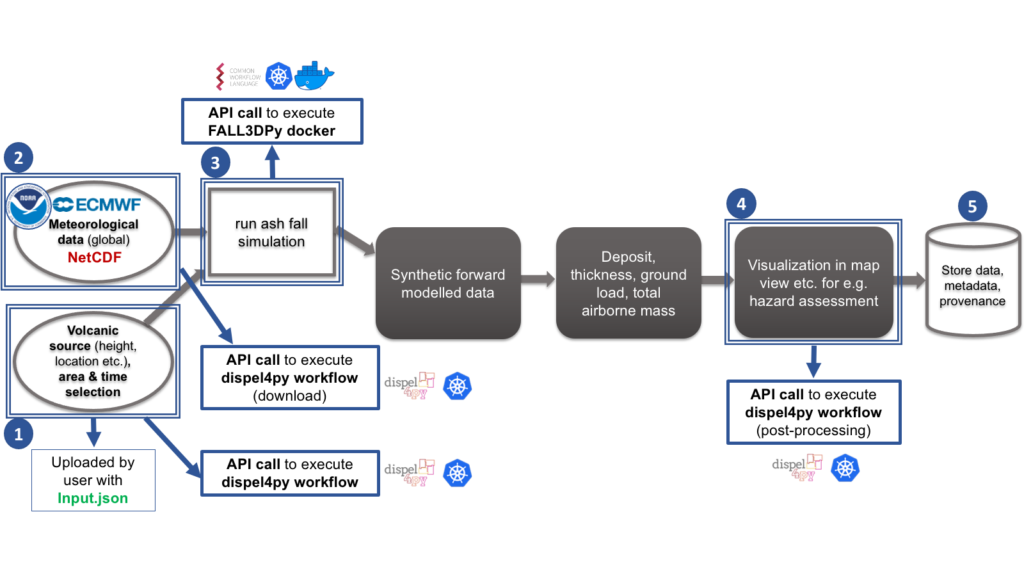
Figure 5: Implementation of the VC test case in the DARE platform
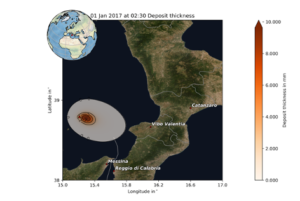
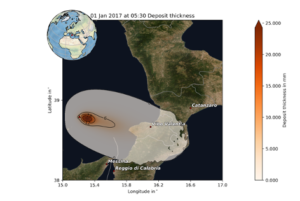
Figure 6 shows the output produced by the VC test case, in this example for an eruption at Stromboli.
Figure 6: Simulation results for the VC test case. Figures show the deposit thickness in mm 2:30 h (left) and 5:30 h (right) after the eruption started for a scenario at Stromboli volcano on 1 January 2017.
Material:
– Jupyter Notebook for VC test case:https://gitlab.com/project-dare/dare-examples/-/blob/master/volcanology/admin/dare_volcanology.ipynb
– dispel4py sub-workflows composing the test case:https://gitlab.com/project-dare/wp6_volcanology/
– FALL3Dpy docker and CWL workflow:https://gitlab.com/project-dare/dare-platform/-/tree/master/containers/exec-context-FALL3DPy